What is the EURIBOR?
EURIBOR stands for “Euro Interbank Offered Rate”. It shows the average of the interest rates set by selected European banks for a certain period of time to make unsecured loans (in euro) to each other. In other words: The EURIBOR is a price determined by the market and based on the base rate.
Why is the EURIBOR relevant for you as a borrower? Many banks use the EURIBOR as a base for setting their variable interest rates. If you choose a variable rate for your loan or during a variable interest period, the EURIBOR is the basis of the interest rate you will have to pay.
Here you can find the current EURIBOR rates.
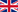
Here you can see how the EURIBOR has changed over the last years. Since 2000, this interest rate benchmark has fluctuated heavily (5% to less than 0%).
3-Month EURIBOR & 12-Month EURIBOR
The term “EURIBOR” is used for five different interest rate benchmarks. These are set for different periods of time: one week, one month, three months, six months or twelve months.
When it comes to loans, the 3-month EURIBOR or the 12-month EURIBOR are used most of the time. The 12-month EURIBOR is almost always more expensive than the 3-Month EURIBOR. The longer the fixed interest period, the more expensive the EURIBOR.